In a distributed environment we will no longer have all functions performed by the same server, Each server will be designated one or more roles.
These roles are also important from a monitoring perspective. As we will see in a later article Splunk’s Monitoring Console will heavily rely on the role a server is given to launch specific searches against it.
Indexer
Indexers are servers that, you guessed it, index data. This means that it’s the instance of Splunk that puts data on disk. It also does the event breaking and time stamp extraction in most cases. Indexers can operate as standalone or a cluster member indexer. Standalone here means that the indexer is NOT replicating any of the data to other indexers. For a clustered indexer this replication will happen with the help of a Cluster Master (which we cover in a later section of this article.
Search Head
A search head’s main activity is taking care of everything related to searches. This included ad hoc searches, reports, dashboards, data models. Search heads can also be clustered into Search Head Clusters
Cluster Master
The cluster master is the brain behind an indexer cluster. It tells the other indexers how and when to replicate to keep the replication factor current and takes care of the searchability factor. Furthermore it will be the single point of contact for the search head in a clustered indexer deployment. It will also play a major role in a feature called indexer discovery. It can tell forwarders which indexers are currently live.
(SHC) Deployer
The deployer is a server that will deploy config file managed apps to a search head cluster. It will NOT, unlike the cluster master for indexer clusters, handle any replication or make sure the cluster is available. Simply put, it’s a deployment server for search head clusters.
Deployment Server
The deployment server is a server that, as the name implies, deploys apps to its clients. In general the clients of a deployment server are universal and heavy forwarders. In bigger clustered deployments as described above, components as the Cluster Master or the Deployer will take care of this for search heads and indexers.
KV Store
KV stores are stored on search heads. We will use KV stores in later articles but for now, remember that they are just ‘fancy’ CSV files put in a database.
Monitoring Console
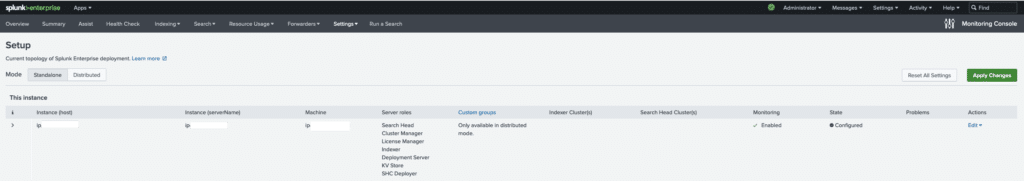
The monitoring console is an app that is installed on every Splunk instance. However, in distributed deployments a designated server is used to monitor all the other servers. Below you can see a screenshot of the general settings screen of a standalone deployment with all roles on the same server. You would never see this in a production instance but imagine that all the roles that you see are configured on dedicated servers.
License Master/Manager
A distributed deployment needs licenses. These licenses are used to determine the volume of data a Splunk deployment ingests on a daily basis. Deployments that violate this license limits will be no longer searchable after 45 warnings in a rolling 60 day period. If your violations occur only on a specific pool, search will be disabled on those license peers only.
More info regarding licensing and violations can be found in Splunk’s License enforcement FAQ.
So that’s an overview of all server roles you will encounter in a distributed Splunk deployment.
As always, you can reach out to me or comment if you have questions, remarks, ….


This post showcases exceptional research and a deep understanding of the subject matter. The clarity of your writing and the…